What Best Describes the Palate Structure of the Mouth
It is distinguished from the hard palate in that it does not have underlying bone. These structures make up the mouth and play a key role in the first step of digestion.

The Oral Cavity Structures Functions Study Com
1 The uvula appears to be split into two parts.

. The roof of the mouth continues posteriorly as the soft palate a flexible fleshy mass of tissues that ends in the uvula. Soft palate The soft palate is a moveable muscular structure. It consists of an anterior hard palate of bone and in mammals a posterior soft palate that has no skeletal support and terminates in a fleshy elongated projection called the uvula.
The anterior region of the palate serves as a wall or septum between the oral and nasal cavities as well as a rigid shelf against which the tongue can push food. It consists of two main parts. 3 The hard palate has a nodular bony ridge.
Anatomy and Histology of Palate Amin Abusallamah 2. Palate in vertebrate anatomy the roof of the mouth separating the oral and nasal cavities. Palatoglossal arch one of a pair of ridges or folds of mucous membrane passing from the soft palate to the side of the tongue.
Innervates the mucosa glands of the soft palate. Describe the structure and composition of nails. The hard and soft palates make up the roof of the mouth.
Absorption which of the following best describes why food moves through the digestive. Hard palate comprised of bone. The palate is a bonymuscular partition that forms the roof of the oral cavity and the floor of the nasal cavities.
What is palate in mouth. Their outer covering is skin which transitions to a mucous membrane in the mouth proper. PAL-et The roof of the mouth.
It creates a division in between the nasal and oral cavities. This arch is called the palate. Subsequently question is where is the Palatoglossal Arch.
The hard palate is a horizontal bony plate that forms a subsection of the palate of the mouth. The hard palate is comprised of two facial bones. Start studying the VN 131 STUDY GUIDE CH.
It acts to separate the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. Introduction The roof of the oral cavity consists of the palate which has two parts-an anterior hard palate and a posterior soft palate. Hard palate The hard palate separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavities.
The cheeks tongue and palate frame the mouth which is also called the oral cavity or buccal cavity. It forms the anterior two-thirds of the roof of the oral cavity. Hard Palate This is a hard bone like structure that sits toward the front of the mouth.
What is the function of the mouth in relation to the digestive system. The soft palate also called the muscular palate or velum is the portion of the roof of the mouth behind the hard palate. The nurse shines a light on the roof of the patients mouth to examine the palate.
The palate completely separates the oral cavity and nasal cavities. The palate also known as the roof of the mouth forms a division between the nasal and oral cavities. Your hard palate is that bony part found at the top of your mouth near the front of your oral cavity.
With a hard palate comes a soft palate located in the back of your oral cavity with a much more fleshy-like surface. Its because of this that humans can not swallow their tongue. Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam.
The hard and soft palates work together to separate the mouth from the nasal cavity. The hard palate contains several landmarks including the incisive foramen and the greater and. The hard palate is the anterior bony portion while the soft palate is the posterior muscular part.
Greater or lesser palatine n. The hard palate and soft palate. The palate is a bonymuscular partition that forms the roof of the oral cavity and the floor of the nasal cavities.
The hard palate What are the different parts of the palate. This region is located at the back of the mouth near the throat. The structures of the mouth are illustrated in Figure 237.
Innervates the mucosa glands of the hard palategingiva until the first premolar. Its anterior two-third is created by the palatine processes of the maxillae and posterior one-third by the horizontal plates of the palatine bones. It consists of two main parts.
THIS MEMBRANE RESEMBLES AN APRON DRAPED OVER THE ABDOMINAL ORGANS OMENTUM WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING REFERS TO THE ROOF OF THE MOUTH PALATE WHICH STRUCTURE CONTAINS THE VILLI MICROVILLI AND BRUSH BORDER CELLS DUODENUM WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING FORM S THE LARGE INTESTINE COLON EMULSIFICATION IS MOST. Which finding would need further investigation. 2 The anterior hard palate is muddy yellow.
This thin connective tissue attaches our tongues to the bottom of our mouth. It is created by the maxillary and palatine bones of the skull and given its bony structure is known as the hard palate. The hard palate which composes two-thirds of the total palate area is a plate of bone covered by a moist durable layer of mucous-membrane tissue which secretes small amounts of mucus.
23 GI flashcards containing study terms like which of the following best describes the chewing of food. It is separated into two distinct parts. Greater or lesser palatine n.
The soft palate sits at the back of the mouth behind the hard palate which. This layer forms several ridges that help grip food while the tongue agitates it during chewing. Your hard palate plays a significant role as it separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity while also aiding swallowing and speaking.
4 The posterior soft palate easily moves up. The palatine rugae are located right behind the upper front teeth in the slope of the palate. The oral cavity is bounded by the teeth tongue hard palate and soft palate.
The term palate describes the roof of the mouth. The mouth is made up of the teeth tongue hard palate and soft palate. What 8 different structures make up the mouth.
The soft palate constitutes the back of the roof of the mouth. Also demarcates the oral cavity from the isthmus of fauces. At the entrance to the mouth are the lips or labia singular labium.
It encloses the palatoglossus muscle and forms the anterior margin of the tonsillar fossa. Unlike the hard palate the soft palate can move. Roof hard and soft palate uvula tonsils salivary glands teeth tongue pharynx epiglottis.
The soft palate moves superiorly during swallowing to cover the nasopharynx of the throat preventing food from entering the nasal cavity. The palatine process of the maxilla and the paired palatine bones. It is seen as a structure with multiple wavy folds of tissue the wrinkles.
The palate is divided into two parts the anterior bony hard palate and the posterior fleshy soft palate or velum. The roof of the mouth is called the palate and hence the name palatine rugae. Greater lesser palatine foramina.
Soft palate comprised of muscle fibres covered by a mucous membrane. Greater or lesser palatine n.

The Oral Cavity Structures Functions Study Com
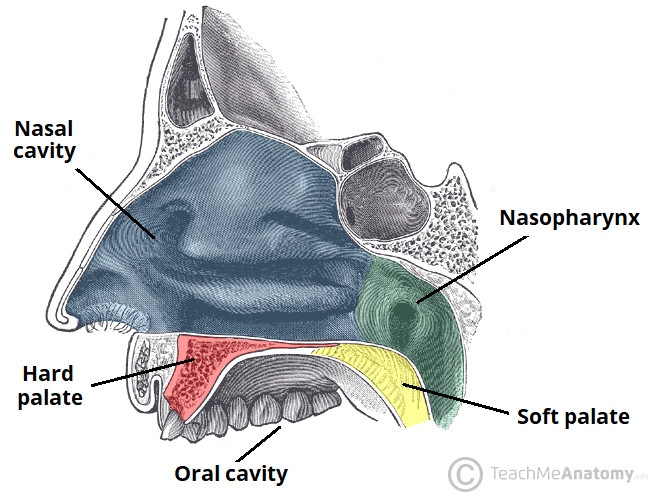
The Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Uvula Teachmeanatomy

Oral Mucosa And Lingual Papillae Keratinised Masticatory Mucosa Covers Download Scientific Diagram
0 Response to "What Best Describes the Palate Structure of the Mouth"
Post a Comment